Technologies
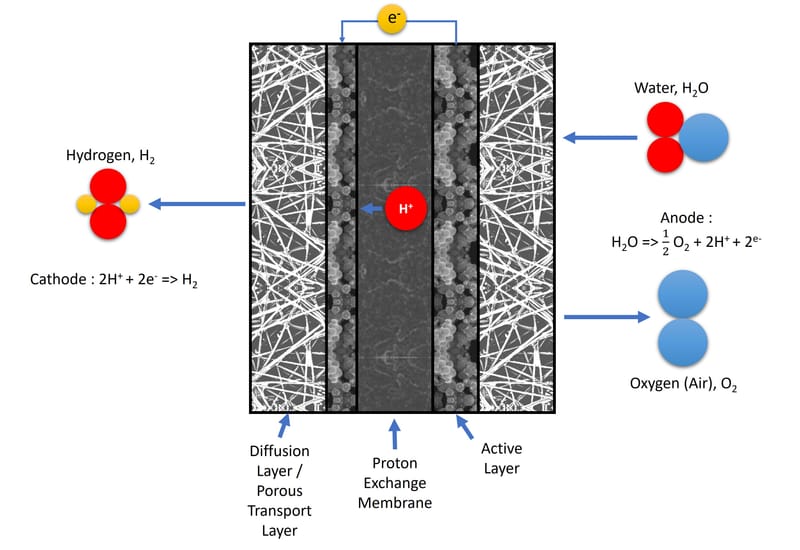
PEM electrolysis
PEM electrolysis is an advanced hydrogen production method that leverages proton exchange membrane (PEM) technology and has rapidly changed the hydrogen production landscape. This process separates water into its two primary elements: hydrogen and oxygen. The heart of this system consists of an anode (positive electrode) and a cathode (negative electrode) separated by a proton-conducting membrane. The anode oxidizes water molecules and separates them into hydrogen ions (H+) and dioxygen (02). Hydrogen ions, or protons, pass through the membrane to the cathode where they are reduced to produce hydrogen gas. The PEM electrolysis process shines in its efficiency, operating at extremely high energy efficiencies, often outperforming traditional electrolysis techniques.
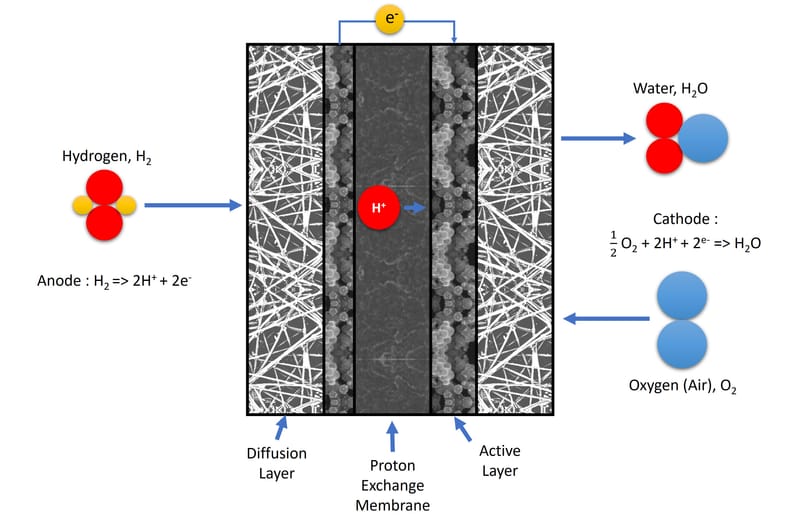
PEM fuel cell
PEM fuel cell technology is an energy solution that redefines the way we harness energy. Using the principle of the proton exchange membrane (PEM), this cutting-edge technology exploits chemical reactions between oxygen and hydrogen to directly generate electrical energy. Unlike traditional energy sources, PEM fuel cell technology is highly efficient, environmentally friendly and emits only water, making it an exceptional choice for applications ranging from heavy mobility applications (land, sea or aeronautics) up to individual or centralized stationary generators.
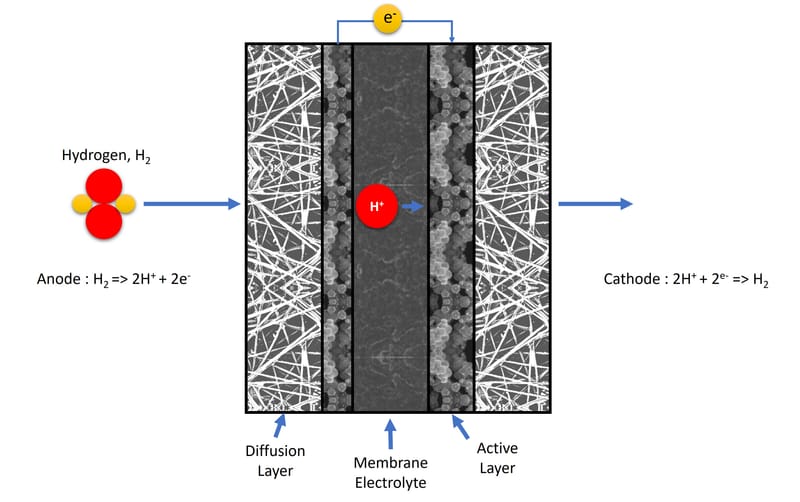
Electrochemical compression
Electrochemical hydrogen compression is a technology aimed at reducing the physical space occupied by hydrogen, in order to ensure efficient storage and transport. This technology uses electrochemical processes to generate hydrogen under pressure, thereby compressing it to a fraction of its original volume. This achieves higher energy density, making this innovative solution ideal for hydrogen fuel cell applications, particularly in the transportation and renewable energy sectors. The service promises high compression efficiency, minimal energy loss and, most importantly, it eliminates the need for mechanical compressors which often result in increased costs and maintenance requirements.